Imagine waking up feeling like you haven’t slept at all, even after a full night in bed. Or maybe your partner has noticed you stop breathing in your sleep. These could be signs of sleep apnea, a common sleep disorder that can have serious effects on your heart.
Sleep apnea happens when your breathing repeatedly stops and starts while you’re asleep. It might sound harmless, but these pauses can put a lot of stress on your body, especially your heart. Think of it like this: your heart needs a steady supply of oxygen to work properly. When your breathing stops, that supply gets cut off, and your heart has to work harder to compensate.
What does this mean for your heart? Over time, sleep apnea can lead to some pretty serious problems:
The Heart of the Matter: Sleep Apnea and Cardiovascular Health
Beyond disrupted sleep, sleep apnea has a significant impact on your cardiovascular health. When breathing repeatedly stops and starts, it disrupts normal blood pressure and oxygen flow to the body. This can lead to:
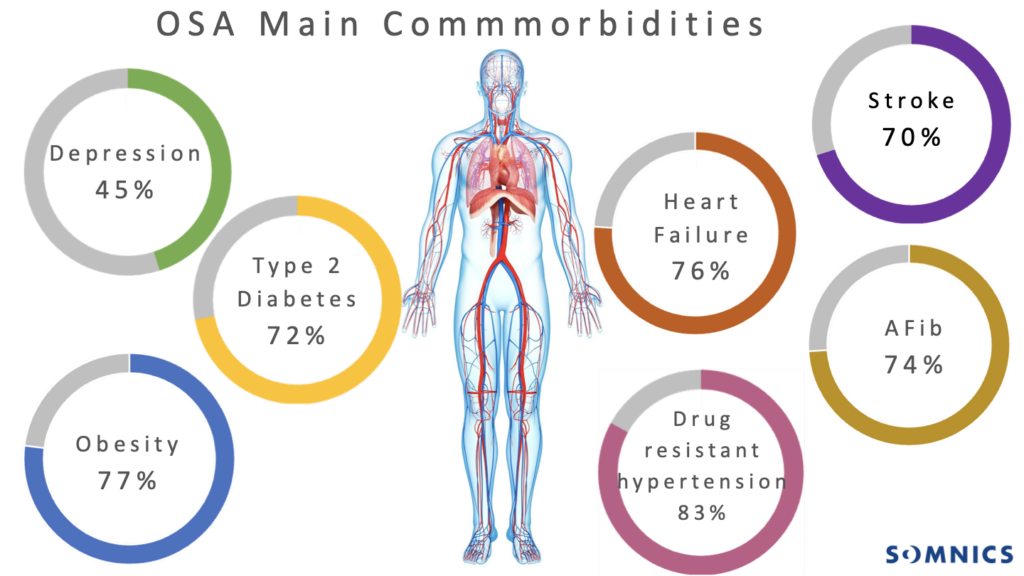
High Blood Pressure: Consistent interruptions to breathing can cause spikes in blood pressure throughout the night.
Irregular Heartbeat (Arrhythmia): The lack of consistent oxygen can lead to abnormal heart rhythms.
Heart Failure: Over time, the constant strain on the heart from sleep apnea can weaken the heart muscle.
Stroke: Sleep apnea increases the risk of stroke by contributing to high blood pressure and blood clots.
Depression: Sleep apnea is often linked to depression due to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue.
Type 2 Diabetes: Sleep apnea can worsen insulin resistance and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Atrial Fibrillation (A Fib): The irregular heart rhythms caused by sleep apnea can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation.
Obesity: Obesity is a major risk factor for sleep apnea, and sleep apnea can also make it more difficult to lose weight, creating a cycle.
Drug-Resistant Hypertension: Sleep apnea can make high blood pressure harder to treat with medication, leading to drug-resistant hypertension.
Finding the Right Treatment for You
While CPAP is a highly effective treatment for many, it’s not always the best fit for everyone. Some individuals may find it uncomfortable, difficult to use consistently, or experience side effects.
Exploring Alternatives: iNAP
For those seeking an alternative to CPAP, iNAP offers a promising solution. iNAP is an FDA-reviewed medical device designed to treat sleep apnea.
Comfortable and Convenient: iNAP provides a comfortable and convenient treatment option without a mask or bulky equipment.
Effective Therapy: iNAP offers a level of therapy comparable to CPAP, helping you breathe easier and improve your sleep quality.
Safe and Well-Tolerated: iNAP is a safe and well-tolerated treatment option.
Prioritizing Your Heart Health
If you suspect you may have sleep apnea or are struggling with CPAP therapy, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. They can diagnose your condition and discuss the most appropriate treatment options for you.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. Consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.